Standalone package based installation
Introduction
This guide will walk you through the process of installing and running Debian packages (.deb) for core, gateway, proxy services on one server - as a simple example.
For production deployment we would recommend to divide services to multiple servers, e.g.:
Defguard Proxy (used for remote enrollment, onboarding and configuring desktop clients) should be on a DMZ node that is exposed in the Internet
Defguard Gateway should be on your firewall/router
Defguard Core (the main control plain panel) - should be in internal network (intranet) and available only by intranet or VPN itself.
We will cover system requirements, additional dependencies, installation steps, and examples of configuration files and step by step running all services. In this example we will use nginx for a web server (proxy) exposing and securing web based services.
Examples will be made by using Debian 12 and Ubuntu based system.
We also provide RPM packages - the procedure is similar to the one for installing DEB packages. If you need help installing RPM packages this guide offers help.
Please also remember to secure the setup after installation.
Hardware Requirements
All Defguard components are very low resource-consuming. All of them are written in Rust and are single binaries. As minimum setup as follows should be more then enough:
CPU
1 GHz
RAM
2 GB (mostly for PostgreSQL)
Disk
2 GB
Architecture
x86_64, ARM64
System Requirements
Before proceeding with the installation, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
Debian-based operating system (Debian, Ubuntu, etc.).
Administrative (sudo) privileges.
A server with a public IP address (and you know what that IP address is and to which interface it's assigned) - in this example we use: 185.33.37.51.
You have a domain name and know how to assign IP and manage subdomains, in our example: Defguard main url will be my-server.defguard.net (and the subdomain is pointed to 185.33.37.51).
Defguard enrollment service (run by proxy) that will enable remote onboarding, enrollment and easy configuration for our Desktop Clients (by adding Defguard instances) with instance URL and one simple token - in this tutorial we use: enroll.defguard.net (this subdomain also points to 185.33.37.51).
If you have a firewall, we assume you have open port 443 in order to expose both Defguard and enrollment service, but also to automatically issue for these domains SSL Certificates. Port 444 (used for internal GRPC communication) should not be exposed public.
System clock is synchronized using Network Time Protocol (NTP). This is important for time-based one-time password (TOTP) codes.
Prerequisites
PostgreSQL
Defguard Core uses PostgreSQL database, so if you do not have installed and configured yet, you can do it in this section. For this tutorial we need to create a user with superuser privileges and database.
First of all, install PostgreSQL package:
Now you can launch a default user and create a new superuser for your database. We create user, password and database with name defguard, beacuse this is by default in /etc/defguard/core.conf, you can change whatever you want.
After creating a user and database we can connect our new user to this database. To make it easier to connect now and then, we could try to add auth file
we created
.pgpassfile that consist of<hostname>:<port>:<database>:<user>:<password>we connected into the
defguarddatabase to verifydefguarduser can communicate with the database
NGINX
To expose our services in the server we need to configure a reverse proxy server. For this we will use nginx web server with ssl certificates for enabling https protocol.
To get started, we need to install:
Enable nginx service
Disable all default domains:
Installing packages
Core service
Navigate to core repository release and choose version of core package that you want to obtain that has debian package and then swap <version> in the following command:
Example:
You can also download directly from the Github realse page, but please note that you should know the path where this could be storead after downloading. Once the package is downloaded, install it using dpkg:
Example:
You can check is core installed properly:
Gateway service
Navigate to gateway repository release and choose version of core package that you want to obtain that has debian package and then swap <version> in the following command:
Example:
You can also download directly from the Github realse page, but please note that you should know the path where this could be storead after downloading. Once the package is downloaded, install it using dpkg:
Example:
You can check is core installed properly:
Proxy service
Navigate to proxy repository release and choose version of core package that you want to obtain that has debian package and then swap <version> in the following command:
Example:
You can also download directly from the Github realse page, but please note that you should know the path where this could be storead after downloading. Once the package is downloaded, install it using dpkg:
Example:
You can check is core installed properly:
Running Defguard
Generating SSL Certificates with Let'sEncrypt
Before we run Defguard and configure the reverse proxy, first let's prepare SSL certificates that will be used by the NGINX service. We will generate a certificate for two domains we use in this example: my-service.defguard.net and enroll.defguard.net:
Certbot will generate certificate in fullchain.pem and privkey.pem in path:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/my-server.defguard.net
/etc/letsencrypt/live/enrolldefguard.net
Core - the control plain
To run core service we need to configure /etc/defguard/core.conf.
To generate any secret (which we recommend to be 64 chars), use the following command:
openssl rand -base64 55 | tr -d "=+/" | tr -d '\n' | cut -c1-64
As previously mentioned, in this tutorial we wil use server domain my-server.defguard.net.
Example /etc/defguard/core.conf:
If you have configured your postgres with different names than in PostgreSQL guide, you can change it in DB configuration part. LDAP configuration is not part of this tutorial, you can also commented those lines.
We will back to this configuration to connect Defguard core with proxy in the Run proxy section. For now DEFGUARD_PROXY_URL is commented.
After changes, you can simply enable and start your Defguard core service:
To see logs, type journalctl command:
Configuring NGINX reverse proxy with SSL
Now, we are able to create our first nginx config for Defguard core service with my-server.defguard.net.
Create config file /etc/nginx/site-available/my-server.defguard.net.conf, example config file for my-server.defguard.ent should look like this:
Link it to /etc/nginx/site-available/
Restart nginx.service to activate changes:
Test your domain on another terminal tab
Success! We can move on to the next service.
If you use this simple setup and run all services on one server, you can use NGINX access restrictions for securing core and allowing to access the my-server.defguard.net only to selected networks - blocking the direct access from the Internet.
Gateway - the WireGuard VPN service
To run gateway, we should do two things:
setup our first location on https://my-server.defguard.net page to get
tokenandgrpc_urlfor gateway service,configure
/etc/defguard/gateway.toml.
Setup location for gateway
Now, after setting up core service you should go to the website that you set on DEFGUARD_URL. The link should redirect you to login page. To log in type these credentials from /etc/defguard/core.conf
login: admin
password:
DEFGUARD_DEFAULT_ADMIN_PASSWORD(by default: pass123)
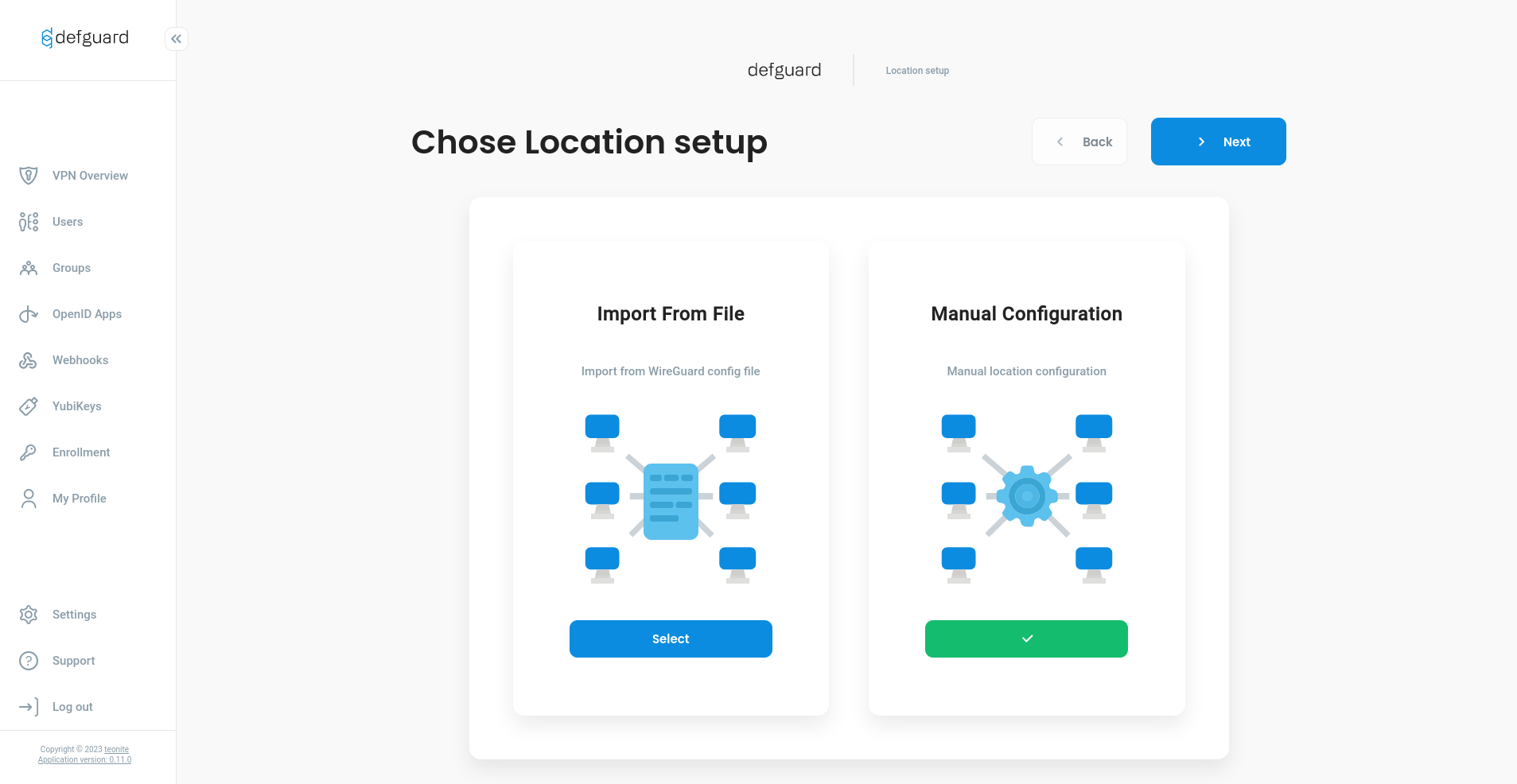
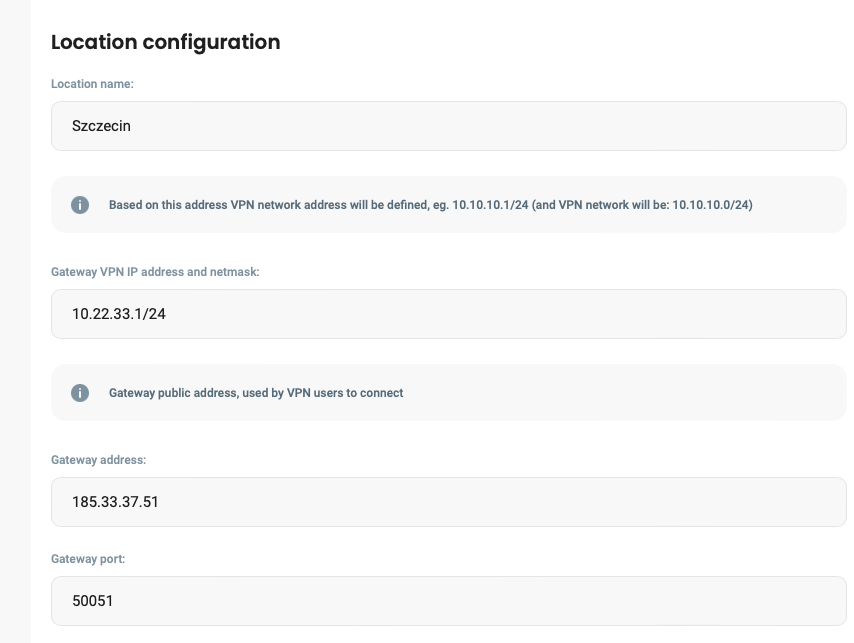
Now we can configure our first location. Depends on what is more convenient for you, choose configuration from Wireguard file or do it manually.
After saving configuration for location you should be redirect to Location overview page, where at the top right corner is Edit Locations Settings button, click on it.
In Gateway server setup copy two variables: DEFGUARD_TOKEN and DEFGUARD_GRPC_URL
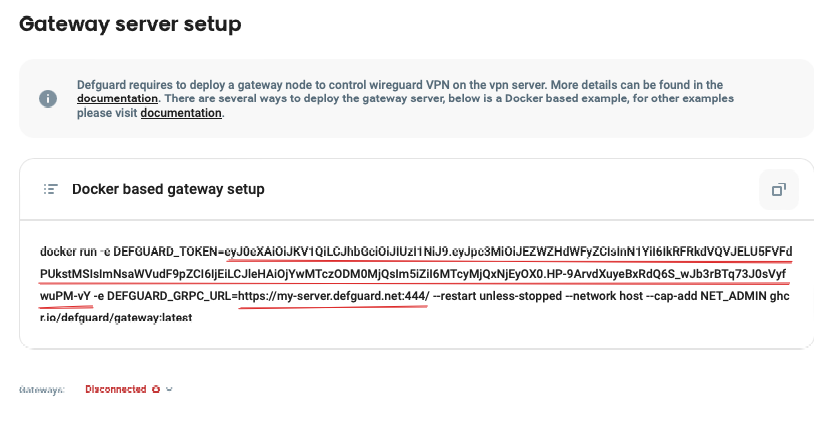
Create config file
After getting DEFGUARD_TOKEN and DEFGUARD_GRPC_URL variables, we can configure our gateway service. Create config.toml file and swap <your_gateway_token> and <defguard_grpc_url> with your values that you copied.
Template for configure gateway service looks like below:
Now we can run gateway service with configuration above:
On the other side, core service should print those informations:
Proxy - enrollment, onboardin and desktop configuration service
To run proxy service (for remote onboarding & enrollment), we can do it by:
Configuring NGiNX reverse proxy for enrollment
Please note that we already have issued the enrollemnt domain SSL certificate.
Create config file /etc/nginx/sites-available/enroll.defguard.net.conf, example config file for enroll.defguard.net should look like this:
Enable configuration and restart nginx:
Enabling Proxy service in the Core
Now, we can update our core configuration in /etc/defguard/core.conf by uncommenting DEFGUARD_PROXY_URL
Full /etc/defguard/core.conf:
Reload changes in /etc/defguarc/core.conf
Now you have full working Defguard services 🥳
You can configure your desktop client using the enrollment service and use your VPN.
If you would like to use the feature in the desktop client to route All traffic through the VPN please configure your firewall to enable Internet access through your VPN - here you can find exaples how to do it.
Securing the setup
After the installation please make sure that only the following ports are open on the server firewall:
HTTPS port for the proxy (and/or the Defguard core if you want it to be public)
VPN server port (eg. WireGuard port)
DO NOT EXPOSE PUBLICLY THE gRPC ports of the core gateway and proxy, which are:
444
50051
50055
Also this setup provides only communication encryption between Defguard components, if you additionally like for core/proxy and gateway to have authorization - please setup a custom SSL CA.
Was this helpful?